Understanding Pre-Engineered Buildings (PEBs): Benefits, Features, and Applications in Industrial Sectors

Introduction to PEB Buildings
What is a PEB Building?
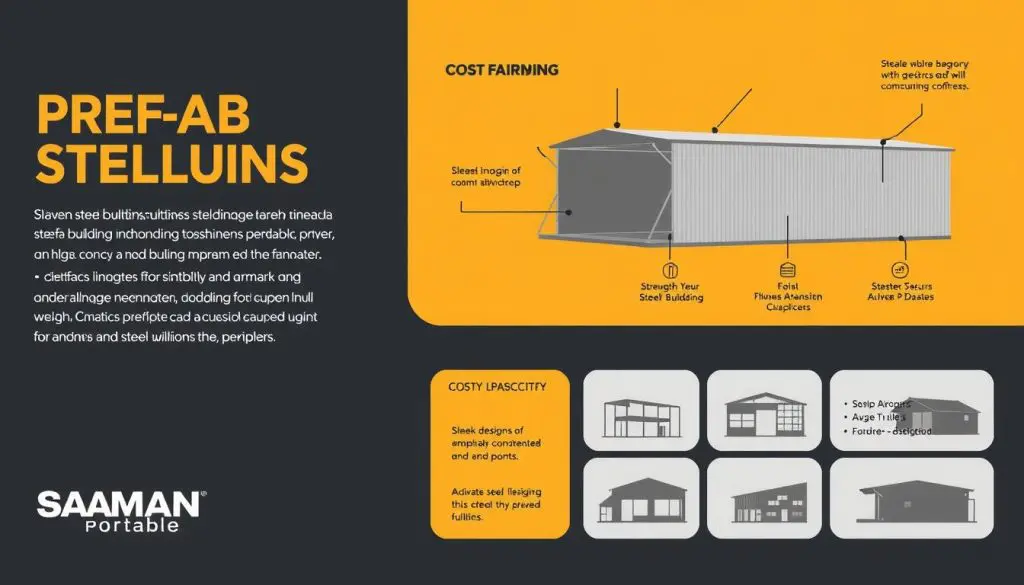
Pre-engineered buildings (PEBs) are structures designed with a streamlined approach that combines precision engineering, factory fabrication, and on-site assembly to provide a durable, cost-effective building solution. Unlike traditional construction methods, which often require lengthy planning and building times, PEBs can be quickly assembled and installed, making them ideal for various sectors, particularly industrial and commercial applications.
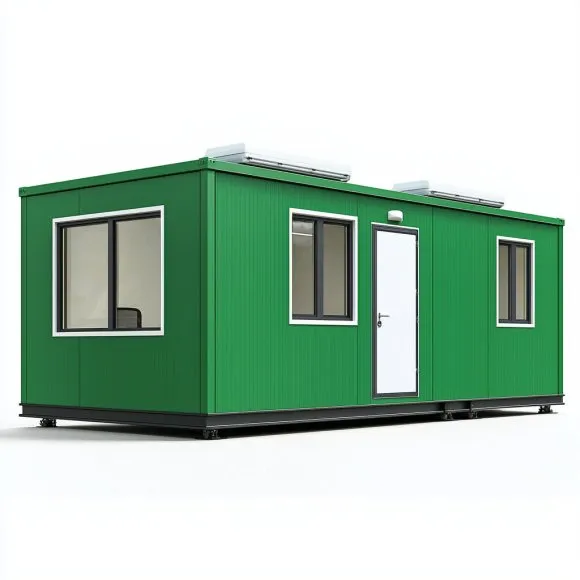
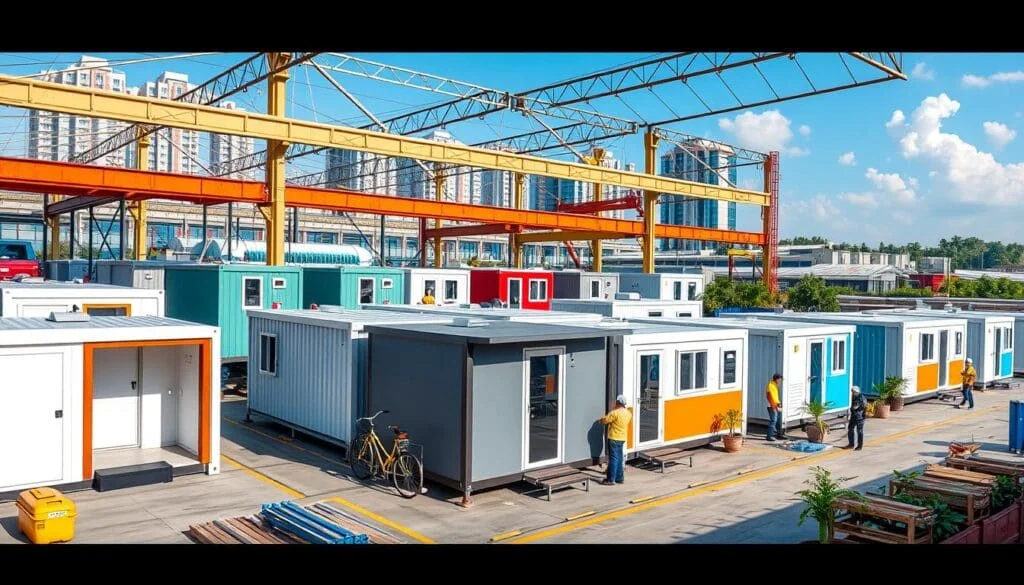
PEBs are made from pre-manufactured steel components that are fabricated in a factory and then transported to the building site for assembly. This efficient method of construction allows for rapid deployment and reduced on-site labor costs, resulting in significant cost savings and shorter project timelines. PEBs are commonly used in the construction of warehouses, factories, and other large-scale industrial facilities. However, their versatility means they can also be used for container houses, prefab buildings, and portable cabins across various sectors.
PEBs in the Construction Industry
Pre-engineered buildings have become increasingly popular within the construction industry due to their high adaptability, speed of construction, and design flexibility. Unlike traditional buildings that require materials to be sourced and fabricated on-site, PEBs are constructed using modular components designed to meet specific structural needs. These modular pieces are manufactured under controlled conditions in a factory and then shipped to the project site. This approach allows for tight quality control and minimal waste, aligning with sustainable building practices. For instance, portable cabins provide flexibility and fast installation, making them suitable for temporary office spaces and site accommodation.
PEBs come with several unique features that make them suitable for a wide range of environments, including robust frames and highly durable panels that can withstand various weather conditions. The growing demand for pre-engineered buildings in industrial sectors can be attributed to the cost-effectiveness and reduced environmental impact of modular construction practices, aligning well with today’s green building standards.
To truly grasp the intricate design aspects, delve into our comprehensive guide on the Design of PEB Structure: Key Elements. This resource will provide you with a deeper understanding of the foundational components that make PEB structures exceptional.
For a holistic understanding of PEB structures, revisit our Design of PEB Structure: Key Elements page. It’s your one-stop resource for all things related to PEB building designs.
Advantages of PEBs Over Traditional Buildings
Pre-engineered buildings offer several advantages over conventional construction methods, such as faster assembly times, reduced waste, and a lower overall cost of ownership. The factory-fabricated components ensure precise measurements and a seamless fit, reducing on-site errors and enabling faster construction times. Additionally, PEBs require less maintenance than traditional buildings, making them an economical choice in the long run. This efficiency is why prefabricated buildings are increasingly favored for industrial and commercial use, especially for projects requiring quick turnaround times and high structural integrity.
Pre-engineered buildings are especially advantageous in industries that require large, open spaces without interior columns or supports, such as manufacturing plants, distribution centers, and sports complexes. Their versatility and ease of installation make them an attractive solution for diverse building needs, from small container houses to large-scale industrial buildings.
Selecting the perfect manufacturer is crucial for your project’s success. Explore our detailed list of PEB Building Manufacturers in India to find trusted partners who can bring your vision to life with precision and expertise.
What is a Pre-Engineered Building (PEB)?

Core Components of Pre-Engineered Buildings
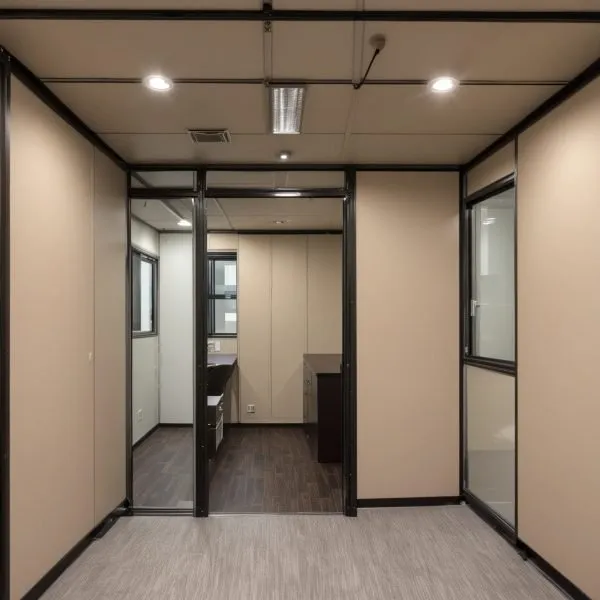
Pre-engineered buildings are constructed from modular components, typically steel, which are designed and manufactured in a controlled environment and then assembled on-site. The main components of a PEB include primary steel frames, secondary members (such as purlins and girts), roof and wall panels, and various accessories for added customization. These elements are meticulously fabricated to precise specifications, enabling a faster and more efficient building process compared to conventional construction.
One key aspect of PEB construction is the use of factory-built steel frames that provide the structure’s core strength. These frames are engineered to carry significant loads and are resistant to environmental factors like strong winds and heavy rain. Secondary members, such as purlins and wall girts, help stabilize the structure while supporting roof and wall cladding. The overall design allows for large, column-free spaces, which makes PEBs highly suitable for applications requiring open floor plans, such as warehouses, workshops, and industrial units.
Thinking about residential projects? Check out our insightful articles on Prefabricated Houses in Hyderabad and Prefabricated Houses in Kerala to discover how PEB buildings can transform residential landscapes
Modular and Adaptable Design
The modularity of PEBs is one of their greatest strengths. They are designed to be flexible and easily expandable, making them ideal for future modifications or extensions. Additionally, the standardized components and pre-manufactured design of PEBs result in a highly adaptable structure that can cater to specific functional needs. For example, porta cabins and portable cabins can serve as temporary offices or on-site accommodations, illustrating the diverse applications that PEB structures can fulfill.
The PEB Construction Process
The construction of a pre-engineered building involves three main stages: designing, fabricating, and assembling.
- Designing: The building design is created based on the specific needs of the project, taking into account load requirements, site conditions, and functional specifications. Detailed blueprints are produced to ensure every component fits precisely.
- Fabricating: The components are manufactured in a factory, ensuring consistent quality and minimizing material waste. This stage allows for strict quality control measures, which enhances the durability and longevity of the final structure.
- Assembling: Once the components are delivered to the site, they are assembled, typically with the help of cranes and bolting systems. This on-site assembly is quick and efficient, often taking just weeks compared to months in traditional construction.
Each of these stages demonstrates the advantages of the PEB approach, combining speed, cost efficiency, and adaptability to deliver a structure that meets modern construction demands. Pre-engineered buildings are widely utilized in various sectors due to these strengths, making them a practical choice for a range of projects, from small prefabricated buildings to large industrial facilities.
How Pre-Engineered Buildings Differ from Traditional Construction
Comparing PEBs with Traditional Construction Methods
Pre-engineered buildings (PEBs) present a modern alternative to traditional construction, significantly altering the approach to building design, materials, and construction timelines. While traditional construction methods involve lengthy processes that include on-site material fabrication, custom measurements, and extended labor hours, PEBs streamline these steps through modular, pre-fabricated components. By producing all primary elements in a factory setting, PEBs reduce the time, cost, and labor associated with conventional construction.
Traditional buildings often require customized materials and numerous subcontractors, contributing to longer timelines and higher overall expenses. In contrast, PEBs are created with standardized components that are manufactured with precision and consistency in a controlled environment, which minimizes errors and project delays. This controlled fabrication also allows PEB structures to be completed in a fraction of the time needed for conventional buildings, making them ideal for urgent projects and sectors where time is a critical factor, such as industrial facilities and commercial retail spaces.
For an extensive overview of prefab housing options, visit our Prefabricated House in Pune Overview. Learn how these solutions can offer both flexibility and durability for your construction needs.
Speed and Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of PEBs over traditional construction is the speed at which projects can be completed. By pre-fabricating all structural elements in a factory, PEBs eliminate many of the delays that arise in traditional on-site construction. Once the components arrive at the site, they can be quickly assembled with minimal on-site labor, often completing in weeks rather than months. This efficiency is especially beneficial for applications requiring swift setup, such as portable cabins for temporary offices or container houses for quick residential solutions.
Environmental and Cost Benefits
PEBs contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing waste and energy consumption. In traditional construction, a significant portion of material waste occurs on-site due to incorrect measurements or material handling inefficiencies. PEBs, however, are fabricated to exact specifications in a factory, leading to lower waste and optimized material usage. Moreover, these structures can incorporate recyclable materials and energy-efficient insulation, which aligns with today’s eco-friendly construction standards.
Cost-wise, PEBs offer financial advantages through reduced material waste, lower labor requirements, and faster project timelines. These factors make PEBs a cost-effective solution, particularly for large industrial applications, where the expenses of traditional construction can escalate quickly. By opting for a pre-engineered building, businesses can achieve significant cost savings while enjoying a high level of structural integrity.
Committed to eco-friendly practices? Learn how to integrate sustainable materials and methods by visiting our Used Containers for Sale in Chennai page, a perfect complement to your PEB projects.
Flexibility and Customization
PEBs also provide flexibility in design and layout, which is more challenging to achieve with traditional building methods. These structures can be customized with a variety of finishes, wall claddings, and roofing options to align with specific functional and aesthetic needs. For example, porta cabins can be customized to function as offices, accommodations, or on-site meeting rooms, showcasing the versatile nature of pre-engineered construction.
Benefits of Pre-Engineered Buildings

Cost-Effectiveness and Budget Efficiency
One of the most attractive advantages of pre-engineered buildings (PEBs) is their cost-effectiveness. Traditional construction projects often suffer from budget overruns due to extended timelines, unpredictable material costs, and labor-intensive processes. In contrast, PEBs utilize a streamlined approach that combines factory manufacturing and on-site assembly, reducing both time and cost. By manufacturing all primary components in a controlled environment, PEBs achieve a high level of efficiency, saving on labor and material waste.
The pre-engineering process minimizes the need for adjustments or repairs on-site, as each component is precisely manufactured according to predetermined specifications. This precision not only accelerates the construction timeline but also avoids many of the unexpected expenses that typically arise in traditional builds. For industrial projects and commercial spaces like portable cabins or container-based structures, these budget efficiencies make PEBs an excellent choice, especially for companies seeking economical yet robust solutions.
Thinking about residential projects? Check out our insightful articles on Prefabricated Houses in Hyderabad and Prefabricated Houses in Kerala to discover how PEB buildings can transform residential landscapes.
Speed of Construction and Installation
Another significant benefit of pre-engineered buildings is the speed at which they can be completed. With all major components fabricated off-site, the time needed for construction is drastically reduced. For example, an industrial PEB warehouse or large-scale storage facility can often be completed in weeks, whereas traditional buildings of similar scale may take several months or even years to finish. Once delivered, the pre-fabricated components are swiftly assembled on-site, resulting in less disruption and quicker readiness for occupancy.
This accelerated timeline benefits industries with urgent infrastructure needs, such as logistics, retail, and construction. Many organizations choose modular prefab buildings for these time-sensitive projects, leveraging the rapid installation to minimize downtime and capitalize on quicker operational startups.
Durability and Low Maintenance
PEBs are engineered to be highly durable, offering robust resistance to extreme weather conditions, seismic activity, and corrosion. Typically made of galvanized steel, PEB structures can endure heavy wind, rain, and temperature variations, making them a practical choice for locations with challenging climates. Additionally, these buildings require less ongoing maintenance compared to traditional structures, due to their corrosion-resistant materials and durable designs.
For example, pre-engineered modular units used in industrial or commercial settings can often go many years without requiring major repairs or structural adjustments. The low maintenance nature of these buildings translates to long-term savings, as business owners avoid the high maintenance costs typically associated with traditional construction.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
In addition to economic and operational benefits, PEBs are recognized for their sustainability. Factory-based fabrication enables better control over resource usage, reducing waste and lowering the building’s overall carbon footprint. Many PEB designs incorporate energy-efficient features, such as advanced insulation and ventilation systems, helping businesses achieve sustainability goals without compromising on structural integrity.
As organizations become increasingly aware of their environmental responsibilities, the demand for eco-friendly building options, such as PEBs, is rising. Their efficient material use, recyclability, and reduced construction waste align well with green building standards and sustainable practices, offering an environmentally responsible alternative to traditional building methods.
Key Features of Pre-Engineered Metal Buildings
Structural Strength and Durability
Pre-engineered metal buildings (PEMBs) are celebrated for their remarkable strength and resilience. Built primarily from high-quality steel, these structures are designed to withstand a wide range of environmental conditions, from heavy rain and strong winds to seismic activity. This makes them particularly suitable for industries where durability is essential, such as manufacturing, warehousing, and large-scale storage. PEMBs are fabricated with load-bearing frames that can support significant weight without additional interior columns, allowing for open, versatile spaces ideal for industrial operations.
The steel frames in PEMBs are treated to resist corrosion and rust, extending the building’s lifespan and reducing long-term maintenance needs. These characteristics are especially beneficial for industries in harsh climates, where traditional building materials may degrade more quickly. With their reinforced steel construction, PEMBs provide a reliable and long-lasting option, similar to modular prefab structures, which can endure demanding environments without compromising structural integrity.
Lightweight Design with High Load-Bearing Capacity
A unique advantage of PEMBs is their lightweight yet strong design. The engineered steel frames are manufactured to provide maximum strength with minimal weight, enabling faster installation without sacrificing stability or durability. This lightweight characteristic also simplifies transportation, making it easier to deliver components to remote or challenging locations. When paired with the simplified assembly process, PEMBs allow for quick setup and efficient site management.
The high load-bearing capacity of these buildings means they can support heavy equipment, extensive storage systems, and other industrial requirements. This flexibility makes PEMBs a top choice for sectors needing large, open areas without internal supports—whether it’s for warehousing, production, or even container-based units used as temporary storage or offices.
Customizable Aesthetic and Functional Options
PEMBs are not just functional; they’re also customizable to meet aesthetic and operational needs. These buildings can be tailored with a wide array of finishes, colors, and design options to suit various industry requirements. From exterior wall panel choices to roof color and texture options, customization allows businesses to create structures that align with their branding or location requirements. Modular office cabins are a great example of how PEMBs can be customized for different uses, from executive offices to employee accommodations.
Functionality is also a key component of PEMB customization. Businesses can include energy-efficient features, such as insulated wall panels, reflective roofing, and ventilation systems to improve energy efficiency and reduce operational costs. This versatility enables companies to build practical, energy-efficient spaces without compromising on aesthetics or usability.
Weather Resistance and Longevity
Another noteworthy feature of PEMBs is their excellent weather resistance, thanks to the robust materials and engineering techniques used in their construction. These buildings can withstand intense conditions, providing security and safety for both occupants and assets. Their resilience is enhanced by high-quality coatings and finishes that further protect against rust, corrosion, and general wear and tear.
PEMBs’ durability and adaptability make them ideal for industrial sectors and other applications requiring robust, resilient structures. Whether used as temporary workspaces or permanent facilities, pre-engineered metal buildings offer a strong, low-maintenance solution for modern industrial needs.
Urban environments require smart solutions. Our Prefab Homes Mumbai Guide provides strategies and designs tailored for the bustling cityscape of Mumbai.
Common Applications of Pre-Engineered Buildings Across Industries

Industrial Applications of PEBs
Pre-engineered buildings (PEBs) are particularly well-suited to industrial settings where their adaptability, strength, and cost-efficiency can be fully leveraged. Industrial PEBs are commonly used for warehouses, manufacturing plants, and production facilities where large open spaces are essential for efficient operations. PEBs provide the flexibility to create expansive, column-free areas that allow for easy movement of machinery, equipment, and storage systems. The durability of PEBs also ensures that they can endure heavy-duty industrial activities without frequent structural repairs or maintenance.
Industries that rely on high-capacity storage, such as logistics, benefit significantly from PEB warehouses. The modular nature of PEBs allows companies to expand facilities as their storage needs grow, without a significant increase in construction time or costs. Many companies now favor pre-engineered warehouse buildings for their ability to handle the demands of high-volume storage and distribution efficiently.
Commercial Uses in Retail and Office Spaces
PEBs are increasingly popular in the commercial sector, where businesses require fast construction timelines and flexible space options. Shopping complexes, office buildings, and retail outlets can be efficiently designed with PEBs to create modern, open-plan spaces. In urban environments, where construction speed and minimal disruption are crucial, PEBs provide a swift solution, allowing businesses to open sooner and with lower upfront costs.
Office spaces within portable modular buildings are also common in sectors that need temporary or semi-permanent setups. For example, retail businesses in pop-up locations or temporary office sites benefit from the quick installation and customization options that PEBs offer. These structures can be outfitted with insulated walls, energy-efficient windows, and climate control features, making them comfortable and functional for both short- and long-term use.
Stay ahead with the latest in construction innovation by exploring our Precast Housing Construction Guide. Discover how precast methods can streamline your building process.
Institutional and Community Buildings
PEBs are widely used for institutional and community buildings, including schools, gymnasiums, auditoriums, and community centers. The versatility and durability of PEBs make them ideal for public facilities that require large spaces for gatherings and events. PEBs can be adapted with specific design requirements, such as seating arrangements, sports flooring, and soundproofing for auditoriums. For schools and community centers, modular prefab classrooms offer a cost-effective way to expand facilities without significant disruptions to ongoing activities.
Agricultural and Storage Facilities
Agriculture is another sector that benefits from the structural flexibility of PEBs. Farmers and agricultural businesses use PEBs for grain storage, livestock shelters, and equipment storage. These buildings are designed to protect sensitive agricultural goods from weather conditions and maintain an optimal environment. PEBs are also customizable for ventilation, which is essential for livestock buildings and crop storage.
Portable storage units and PEB barns offer farmers a practical solution for keeping equipment, crops, and livestock safe and organized. Additionally, the easy expansion options allow agricultural businesses to scale their storage capacity according to changing needs, without facing the high costs associated with traditional building extensions.
Enhance your agricultural projects with our Prefab Farm Homes India Guide. This guide offers valuable insights into leveraging PEB structures for efficient and sustainable farm housing.
Conclusion
The diverse applications of PEBs demonstrate their flexibility and effectiveness across multiple industries. From robust industrial warehouses to adaptable retail spaces, pre-engineered buildings have become a valuable solution for modern construction needs, providing durable, customizable, and cost-effective structures across sectors.
Focus on Industrial PEB Buildings
Why Industrial Sectors Prefer Pre-Engineered Buildings
Industrial sectors, especially those requiring large-scale, durable, and open space structures, are some of the most enthusiastic adopters of pre-engineered buildings (PEBs). The unique design flexibility and structural strength of PEBs make them ideal for heavy-duty applications, from manufacturing plants to logistics and distribution centers. Industrial PEB buildings can support substantial equipment loads and large machinery, allowing industries to maximize productivity within a well-organized, spacious environment.
One of the reasons why industrial facilities favor PEBs is the speed of construction and installation. Unlike conventional building methods that may take years to complete, PEBs can be operational within weeks, ensuring minimal disruption to business operations. This rapid setup is essential for industries that require quick expansion to meet growing demand. For instance, pre-engineered factories are an ideal solution for businesses that need extra production capacity or storage space on short notice.
PEBs in Manufacturing Facilities
Manufacturing facilities often rely on PEBs due to their ability to offer expansive, unobstructed spaces, which are crucial for efficient workflows. In traditional buildings, interior columns can limit floor space and restrict the placement of heavy machinery. PEBs, however, allow for large open spans without columns, making it easier to organize machinery, assembly lines, and storage zones in an optimal layout. Furthermore, the load-bearing capability of customized industrial metal buildings supports heavy-duty equipment without compromising the structural integrity.
Another critical benefit for manufacturing facilities is the low maintenance requirement of PEBs. With steel components treated to withstand corrosion and environmental wear, industrial PEB buildings are more resilient and cost-effective over time. This durability reduces the need for frequent repairs and lowers the total cost of ownership, enabling manufacturing businesses to allocate more resources toward operations rather than building upkeep.
PEBs for Warehousing and Logistics
Warehousing and logistics are other industrial sectors where PEBs are increasingly valuable. Warehouses often require large, high-capacity storage areas that can support racking systems, loading docks, and heavy inventory. PEB warehouses can be customized to incorporate features such as high ceilings, reinforced floors, and wide entry points for loading vehicles. This makes them exceptionally suited for storing large volumes of goods efficiently.
Additionally, the scalability of PEBs allows logistics and warehousing companies to expand their facilities as storage needs grow. Unlike traditional warehouses that would require extensive renovations, PEBs are designed with modular components that can easily be expanded or reconfigured. Modular storage buildings offer a flexible solution for adjusting storage capacity to align with seasonal or business fluctuations, making them a highly practical option for the logistics industry.
Heavy Industrial Applications and Specialized Needs
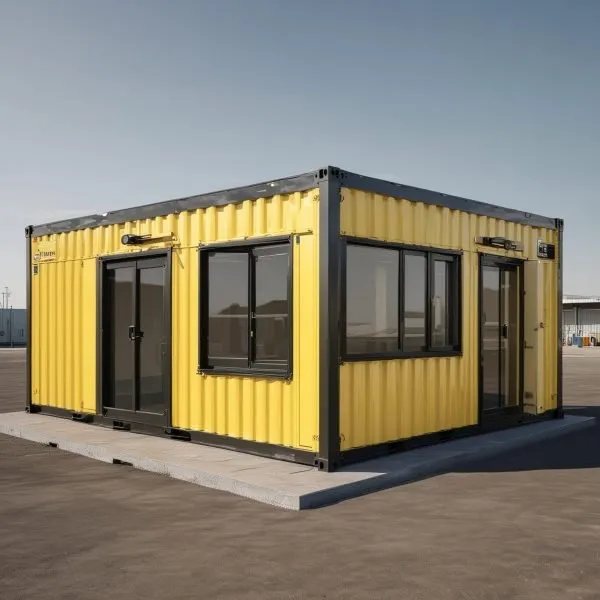
For heavy industries like oil and gas, mining, and energy, PEBs offer solutions that are both resilient and adaptable to remote or challenging locations. The modular construction of PEBs allows for efficient transportation and assembly, even in rugged terrains or areas with limited access. This adaptability is beneficial for temporary structures or long-term facilities that need to withstand harsh weather conditions and frequent relocation. Portable industrial units are a preferred choice for remote industrial sites, as they provide essential shelter and operational spaces while remaining easy to move or expand.
Overall, industrial PEB buildings bring together the durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness needed for high-performance applications, offering a reliable and scalable building solution tailored to the specific demands of industrial environments.
PEB Design Process and Engineering Considerations

The Design and Engineering Phases of PEBs
Designing a pre-engineered building (PEB) is a highly specialized process involving careful planning, detailed engineering, and precision manufacturing. Unlike traditional construction, where each building is custom-built on-site, PEBs use a modular design approach, allowing for streamlined and efficient construction. The design process for a PEB begins with defining the building’s purpose, which informs the layout, structural needs, and customization options. Engineers work closely with architects and clients to produce a design blueprint that considers functional requirements, environmental factors, and aesthetic preferences.
Once the design is finalized, detailed engineering calculations are conducted to ensure that the building can withstand various loads, including wind, seismic activity, and snow. Structural engineers design load-bearing elements such as columns, beams, and roof systems to create a durable framework that meets all safety and regulatory standards. This meticulous design process is crucial for sectors requiring robust buildings, like industrial warehouses and manufacturing facilities, where structural integrity is non-negotiable.
Fabrication and Quality Control in PEBs
After the design and engineering stages, the fabrication of PEB components takes place in a controlled factory environment. This off-site manufacturing ensures high-quality production, as components are made to precise specifications under strict quality control measures. In a factory setting, variables such as temperature, humidity, and handling can be managed, resulting in superior product consistency and durability. This process also minimizes waste, aligning with eco-friendly building practices that reduce environmental impact.
Each structural element, from steel frames to wall panels, is crafted according to the design blueprint and then shipped to the construction site. By manufacturing components off-site, PEBs can be assembled quickly and efficiently upon delivery. This approach is particularly beneficial for projects that need to be completed in tight timelines, such as temporary on-site accommodations or emergency response facilities.
Customization Options and Functional Design Elements
One of the most attractive features of PEBs is the ability to customize structures to meet specific functional and aesthetic needs. PEBs offer a wide range of options, including insulated wall panels, energy-efficient roofing, and customizable color schemes. Functional elements, like HVAC systems, skylights, and ventilation, can be seamlessly integrated into the design, allowing PEBs to adapt to diverse requirements. For instance, modular office cabins can be outfitted with climate control and soundproofing to create comfortable working spaces in industrial settings.
Customizable interiors make PEBs suitable for a variety of uses, from open manufacturing floors to partitioned office spaces. In addition, PEBs can be designed to accommodate future expansions, providing businesses with flexibility as they grow. Unlike traditional buildings that require extensive renovations to expand, pre-engineered buildings can be easily modified with additional modules, making them an ideal solution for growing commercial facilities.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
PEBs are designed to meet all necessary regulatory codes and safety standards, which vary based on geographic location and building purpose. Engineers ensure that PEBs comply with local regulations, including building codes for wind and seismic load resistance. This compliance is especially important in industrial sectors where safety is paramount, and buildings are often subjected to intense use. High-quality pre-engineered modular buildings are built to be safe, sustainable, and resilient, making them suitable for both temporary and permanent applications in various industries.
Overall, the design and engineering process of PEBs provides a robust foundation for creating functional, efficient, and customizable buildings that meet industry standards and offer versatility for different sectors.
Challenges and Limitations of Pre-Engineered Buildings
Design Limitations and Customization Constraints
While pre-engineered buildings (PEBs) offer numerous advantages in terms of speed, cost, and efficiency, they may come with certain design limitations. PEBs are primarily modular, which can restrict customization to some extent. Although PEB manufacturers offer various customization options, such as cladding styles, roof shapes, and wall finishes, highly specialized architectural designs or unconventional layouts may be challenging to achieve. For instance, structures that require complex facades or unique aesthetic features might find traditional construction methods more accommodating.
These design constraints can be a drawback for businesses seeking unique or highly tailored buildings, especially in commercial sectors where brand image and architectural design are significant. However, for industrial applications, where functionality often takes precedence over aesthetics, PEBs remain an ideal solution. Standard industrial structures, such as warehouses and storage units, benefit from the modular efficiency of PEBs despite these minor limitations.
Higher Initial Costs for Customization
Though PEBs are known for their cost-efficiency, the price can increase with customization. Adding unique design features or high-end finishes can raise initial costs, sometimes making PEBs less economical compared to conventional buildings. For instance, integrating premium energy-efficient materials or advanced HVAC systems may increase costs for customized modular offices. Businesses that need very specific, non-standard elements should evaluate whether the initial investment aligns with their budgetary requirements.
For larger industrial projects or warehouses that prioritize scale and speed over intricate design details, the modular nature of PEBs provides significant savings. However, for companies focused on extensive customization, particularly in sectors like hospitality or retail, the potential for additional costs should be considered.
Insulation and Acoustic Challenges

Another limitation often noted with PEBs is related to insulation and acoustic performance. Since most PEBs use metal panels for walls and roofs, they may not naturally offer the same insulation properties as traditional materials like concrete or brick. Without added insulation, PEBs may experience temperature fluctuations, which could impact energy efficiency. Similarly, metal surfaces may not provide optimal acoustic insulation, leading to noise reverberation issues inside the building.
However, these challenges can be mitigated with additional layers of insulation or specialized acoustic treatments, albeit at an extra cost. Many pre-engineered office cabins, for example, are now designed with insulated wall panels and soundproofing solutions to enhance interior comfort. These adjustments, though beneficial, can add to the overall project cost and may be necessary for buildings located in extreme climates or in noise-sensitive areas.
Transport and On-Site Assembly Constraints
While PEBs are typically faster to install than traditional buildings, certain logistical challenges can arise in remote or inaccessible locations. Transporting large prefabricated components over long distances may involve significant shipping costs, especially for rural or international projects. Additionally, on-site assembly requires adequate space for storage and crane operation, which can be limited in crowded urban areas. These logistical factors may impact the feasibility of PEB projects for some businesses.
For organizations located in remote areas, modular container structures can provide a practical solution by offering compact, easily transportable units. However, for large-scale PEB installations, companies must carefully plan logistics and site accessibility to ensure seamless delivery and assembly.
Structural and Environmental Limitations
Finally, while PEBs are designed to be robust, they may have limitations when it comes to extreme or highly variable environmental conditions. For instance, in regions with extremely high wind loads or seismic activity, additional structural reinforcements may be required, potentially increasing the building’s cost. Similarly, PEBs might need enhanced corrosion protection in areas with high humidity or salt exposure.
Overall, while PEBs offer substantial benefits, understanding and addressing these potential limitations is crucial for businesses considering this construction method. For industries that prioritize adaptability and efficiency, such as industrial storage facilities, PEBs remain a highly viable and beneficial option despite these challenges.
Future of Pre-Engineered Buildings and Emerging Trends
Technological Advancements in PEBs
The future of pre-engineered buildings (PEBs) is heavily influenced by advancements in digital construction technologies like Building Information Modeling (BIM), which allow for detailed planning and reduced errors. BIM technology enhances collaboration and precision, proving particularly beneficial for complex structures like industrial warehouses. Additionally, PEBs are now integrating energy-efficient materials, such as advanced insulation and solar panels, to meet the growing demand for sustainable, cost-effective building solutions.
Growing Demand for Sustainable PEB Solutions
As sustainability becomes a priority for businesses, PEB manufacturers are increasingly focusing on recyclable materials and energy-efficient building designs. Many green modular structures now incorporate renewable energy sources like solar power, which aligns with global environmental goals and reduces operating costs. For more about our commitment to sustainable and innovative building solutions, visit our About Us page.
Hybrid PEB Designs and Multi-Use Spaces
PEBs are evolving to meet the needs of businesses requiring adaptable, multi-use spaces. Hybrid PEBs, which blend traditional materials like wood or concrete with steel framing, are gaining popularity for creating both functional and visually appealing spaces. These hybrid designs are especially popular in commercial areas where flexibility and aesthetics are essential. Modular retail buildings are one example, catering to retail, hospitality, and mixed-use developments.
Increased Focus on Resilient and Disaster-Ready Structures
PEBs are also adapting to withstand extreme weather, making them ideal for disaster-prone regions. Engineers now design reinforced PEB structures that can resist high wind loads, seismic activity, and other natural events, making them highly valuable for emergency response facilities and resilient infrastructure. For instance, modular emergency shelters provide reliable, durable accommodation for disaster relief and rapid deployment situations.
1. What are PEB buildings?
PEB buildings, or Pre-Engineered Buildings, are structures manufactured with prefabricated steel components that are assembled on-site. They are known for their cost-effectiveness, speed of construction, and durability.
2. How do PEB buildings differ from conventional buildings?
Unlike conventional buildings, which require custom fabrication and lengthy on-site construction, PEB buildings are pre-designed and manufactured in a factory, then quickly assembled on-site. This reduces construction time, labor costs, and material waste.
3. What are the main applications of PEB buildings?
PEB buildings are versatile and used across various sectors, including industrial warehouses, factories, logistics facilities, agricultural storage, retail spaces, and community buildings.
4. What are the primary benefits of PEB buildings?
PEB buildings offer benefits like reduced construction time, cost savings, high durability, low maintenance, flexibility in design, and easy expansion options. They are also environmentally friendly due to reduced material waste.
5. Can PEB buildings be customized for specific needs?
Yes, PEBs are highly customizable. They can be tailored with various finishes, roof shapes, wall claddings, insulation, and functional features to meet specific operational and aesthetic requirements.
6. Are PEB buildings energy efficient?
PEBs can be designed with energy-efficient features, such as insulated walls, cool roofing systems, and solar panel integration, to reduce energy costs and improve sustainability.
7. How durable are PEB buildings in extreme weather conditions?
PEB buildings are engineered to withstand extreme weather, including high winds, rain, snow, and even seismic activity. The steel structure and optional protective coatings provide excellent resistance to corrosion and environmental wear.
8. How long does it take to construct a PEB building?
PEB buildings have significantly shorter construction timelines compared to traditional structures. Depending on the project’s size and complexity, they can be completed in weeks rather than months.
9. Are PEB buildings suitable for temporary and portable structures?
Yes, PEBs are ideal for temporary and portable structures. They can be easily assembled, disassembled, and relocated, making them suitable for portable offices, container homes, and site cabins.
10. Are PEB buildings environmentally sustainable?
PEB buildings are sustainable as they reduce material waste through prefabrication and can incorporate recyclable materials. Their energy efficiency options also contribute to a lower environmental footprint.
 Container Cafe
Container Cafe